d
Size: a a a
2020 May 18
⠀
Юзать лодаш в 2020 — моветон
а что должно быть вместо его
S
аналогичный дебаунс со стаковерфлоу
export function debounce (fn, delay) {
var timeoutID = null
return function () {
clearTimeout(timeoutID)
var args = arguments
var that = this
timeoutID = setTimeout(function () {
fn.apply(that, args)
}, delay)
}
}
CM
that :D
+
DE
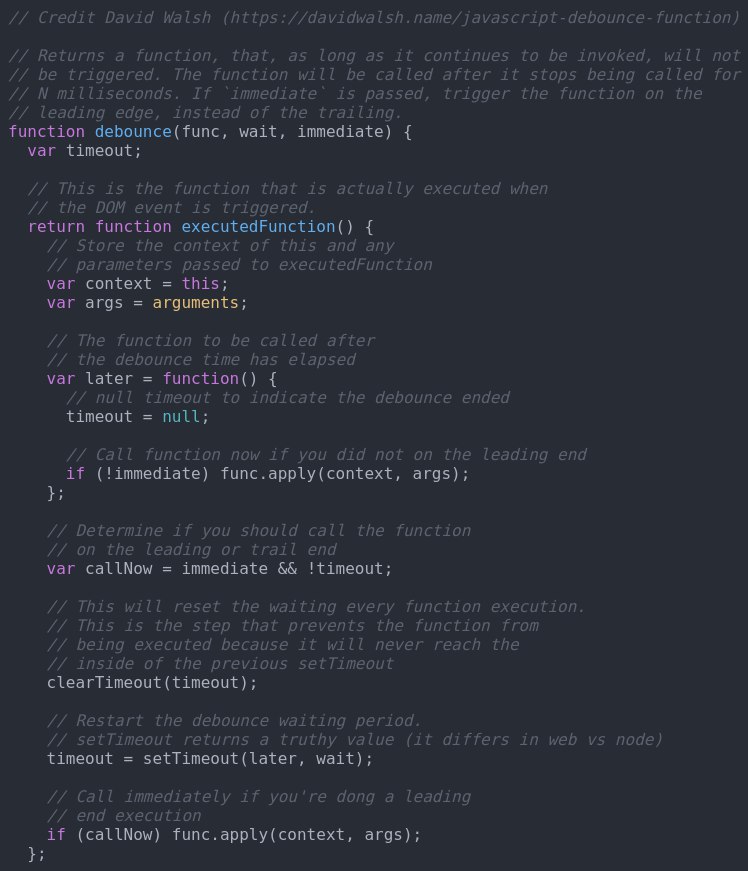
// Credit David Walsh (https://davidwalsh.name/javascript-debounce-function)
// Returns a function, that, as long as it continues to be invoked, will not
// be triggered. The function will be called after it stops being called for
// N milliseconds. If `immediate` is passed, trigger the function on the
// leading edge, instead of the trailing.
function debounce(func, wait, immediate) {
var timeout;
// This is the function that is actually executed when
// the DOM event is triggered.
return function executedFunction() {
// Store the context of this and any
// parameters passed to executedFunction
var context = this;
var args = arguments;
// The function to be called after
// the debounce time has elapsed
var later = function() {
// null timeout to indicate the debounce ended
timeout = null;
// Call function now if you did not on the leading end
if (!immediate) func.apply(context, args);
};
// Determine if you should call the function
// on the leading or trail end
var callNow = immediate && !timeout;
// This will reset the waiting every function execution.
// This is the step that prevents the function from
// being executed because it will never reach the
// inside of the previous setTimeout
clearTimeout(timeout);
// Restart the debounce waiting period.
// setTimeout returns a truthy value (it differs in web vs node)
timeout = setTimeout(later, wait);
// Call immediately if you're dong a leading
// end execution
if (callNow) func.apply(context, args);
};
S
// Credit David Walsh (https://davidwalsh.name/javascript-debounce-function)
// Returns a function, that, as long as it continues to be invoked, will not
// be triggered. The function will be called after it stops being called for
// N milliseconds. If `immediate` is passed, trigger the function on the
// leading edge, instead of the trailing.
function debounce(func, wait, immediate) {
var timeout;
// This is the function that is actually executed when
// the DOM event is triggered.
return function executedFunction() {
// Store the context of this and any
// parameters passed to executedFunction
var context = this;
var args = arguments;
// The function to be called after
// the debounce time has elapsed
var later = function() {
// null timeout to indicate the debounce ended
timeout = null;
// Call function now if you did not on the leading end
if (!immediate) func.apply(context, args);
};
// Determine if you should call the function
// on the leading or trail end
var callNow = immediate && !timeout;
// This will reset the waiting every function execution.
// This is the step that prevents the function from
// being executed because it will never reach the
// inside of the previous setTimeout
clearTimeout(timeout);
// Restart the debounce waiting period.
// setTimeout returns a truthy value (it differs in web vs node)
timeout = setTimeout(later, wait);
// Call immediately if you're dong a leading
// end execution
if (callNow) func.apply(context, args);
};
DE
Всё понятно
Но раздуто слишком
Но раздуто слишком
Для тебя дули
DE